Cat of the Month ~ January 2017
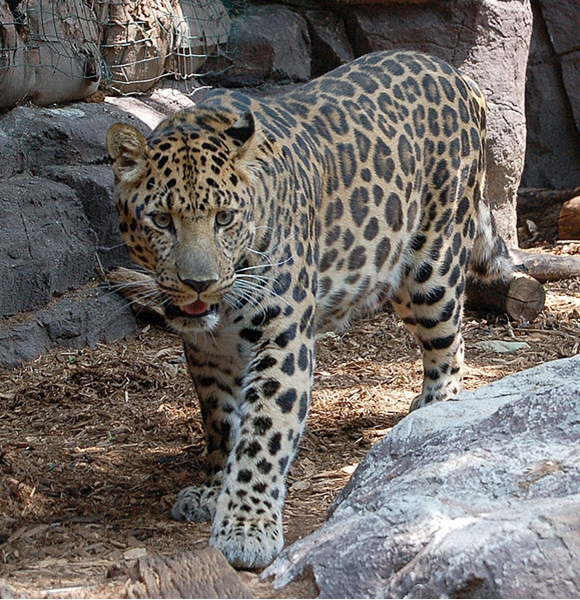
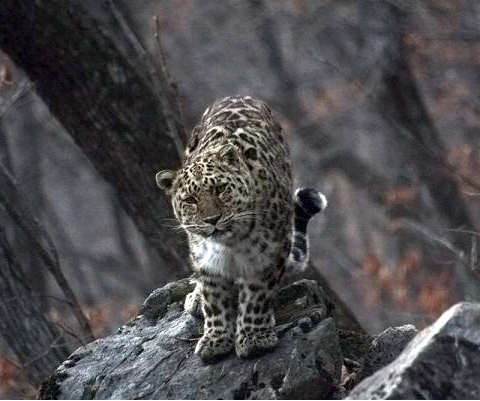
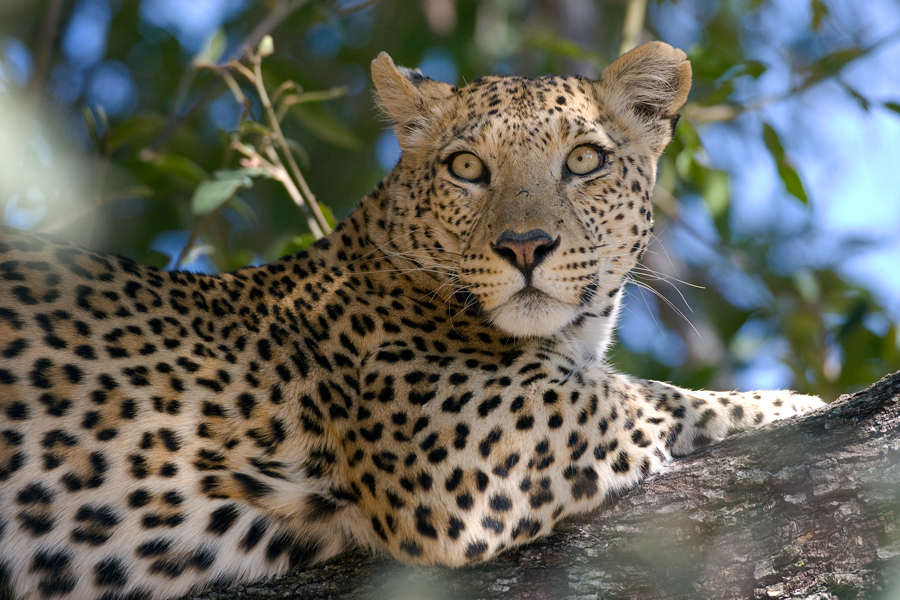
The Far Eastern leopard (Pantera pardus orientalis) is the rarest surviving subspecies of leopard. The only surviving Far Eastern leopard population is in the southern Far East of Russia. Today it numbers between just 30 and 50 animals.
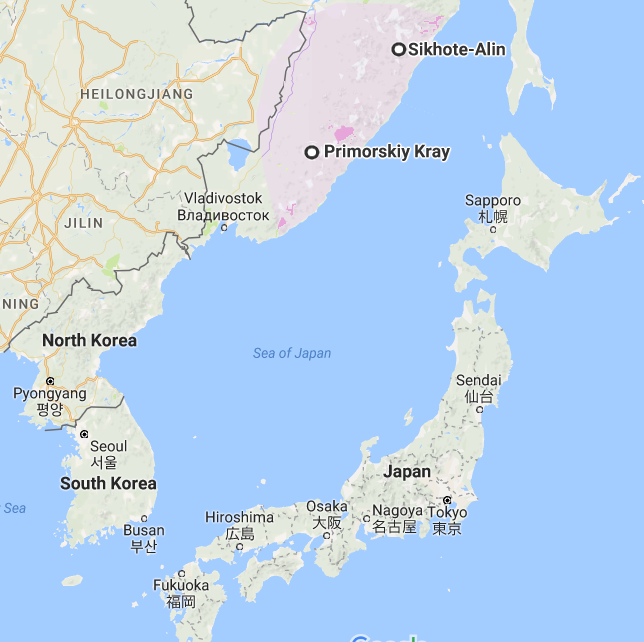
It was only in 1972 that collected information on the rare Far Eastern wild cat was summarised in an official document by Vladimir Geptner and Arkady Sludsky. It noted that only three isolated groupings of Far Eastern leopards exist in the Far East: at Prikhankaisky, in southern Sikhote-Alin, and one in the Nadyozhdinsky and Khasansky Districts in the southwest of the Primorye Territory.
The Far Eastern leopard used to live at the Komarov Ussuri State Nature Reserve and was an unprotected species both in the reserve and in the surrounding areas. During the 1930s and 1940s all predators, including the leopard, were routinely destroyed, both at the Ussuri and other nature reserves. From 1956, hunting leopards was officially outlawed, but the economic development of the leopard’s natural habitat, especially deer parks, had a negative impact on the stability of the population. These factors, together with a sharp increase in poaching, led to a significant decline in the population and a sharp decrease in the geographical range inhabited by the leopard. It’s notable that the Eastern Leopard also shares its habitat with the Siberian Tiger, which likely competes for available prey stocks.
Detailed studies of the current distribution, numbers, and structures of the populations, the social organisation, reproduction, food and other biological characteristics of the Far Eastern leopard were conducted in 1976 by Dmitry Pikunov and then subsequently in 1986 by Viktor Korkishko. The completion of these studies led to the publishing in 1992 of the document ‘The Far Eastern Leopard’, which presented the most comprehensive information to date on the Far Eastern leopard.
Study
Between 1993 and 1998 a project was carried out in Russia which focused on studying the size and structure of the habitats of Far Eastern leopards using VHF transmitter collars.
Over the last 10 years the study of the Far Eastern leopard population has focused on determining the numbers of the subspecies using a variety of approaches, chief among them the traditional method of tracing their tracks and photo identification of the animals with the use of camera traps. A study to determine the status of the Far Eastern leopard using molecular genetic techniques has begun, and comprehensive veterinary studies have also been carried out.
Warning Signs
Today there is only one population of the Far Eastern leopard, numbering somewhere between 40 and 52 animals. This rare species of wild cat has been included on the Red List of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and is in danger of extinction.
In recent years the leopards’ food supply has shrunk considerably due to forest fires and the development of the infrastructure of the Primorye Territory. As a result of the economic development of the forests and poaching, the leopard’s main food source, the roe deer, is slowly being destroyed.
Some Good News
If urgent measures are not taken to preserve these animals, the Far Eastern leopard population will die out. In connection with this, in 1999 the Strategy for the Preservation of the Far Eastern Leopard in Russia was adopted. This strategy proposes improving the network of leopard reserves (specially protected natural areas), optimising wildlife management in the leopard’s habitats, creating a viable population in captivity and reviving the dwindling population in the wild. The strategy also suggests that the numbers of leopards and the state of their habitats should be monitored, research studies conducted and measures to preserve the leopard promoted.
Original Article:
Please visit the above website for much more information and many more photos and video of this beautiful creature.